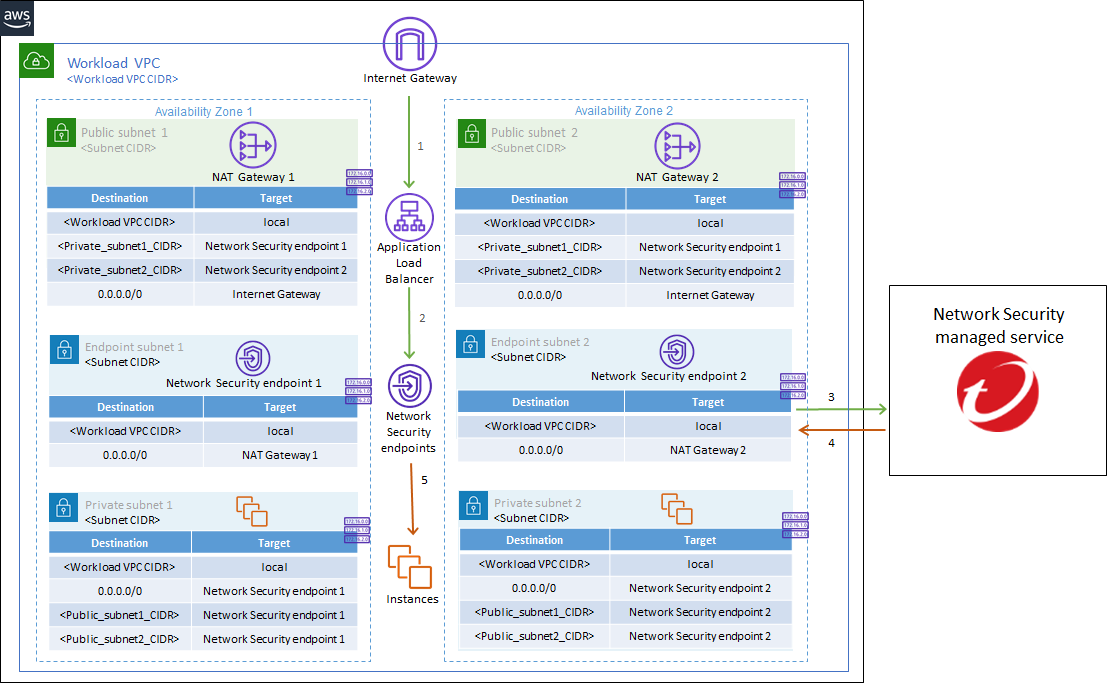
Environments that use an Application Load Balancer (ALB)
This configuration is best suited for cloud environments with assets located behind an Application Load Balancer (ALB). ALBs enable TLS termination for encrypted IPv4 traffic to help with TLS inspection as well as more specific routing so that traffic can be distributed to multiple targets and AZs in your environment. Learn more about how Application Load Balancers are supported in AWS.
These type of environments typically include “Workload” VPCs, which are VPCs with public facing assets, as well as an Internet Gateway. Each AZ within the VPC also includes a NAT gateway and public and private subnets with a default route table for each.
In this deployment type, traffic flows from the Internet Gateway to the Workload VPC using the ALB and the NAT gateways. The ALB then distributes the traffic to the resources in the various Workload VPC AZs. After Network Security managed service is deployed, this traffic is diverted to managed service for inspection after the traffic passes through the ALB.
Environments without an ALB
This configuration is best suited for cloud environments that include public facing assets, which need protection from inbound internet traffic, but that do not use an ALB. These types of environments typically include “Workload” VPCs, which are VPCs with public facing assets, as well as an Internet Gateway and a public subnet with a route table.
In this deployment type, traffic flows into the Workload VPC from the Internet Gateway to your public facing assets. After Network Security managed service is deployed, this inbound traffic is diverted to managed service for inspection before reaching your public assets.
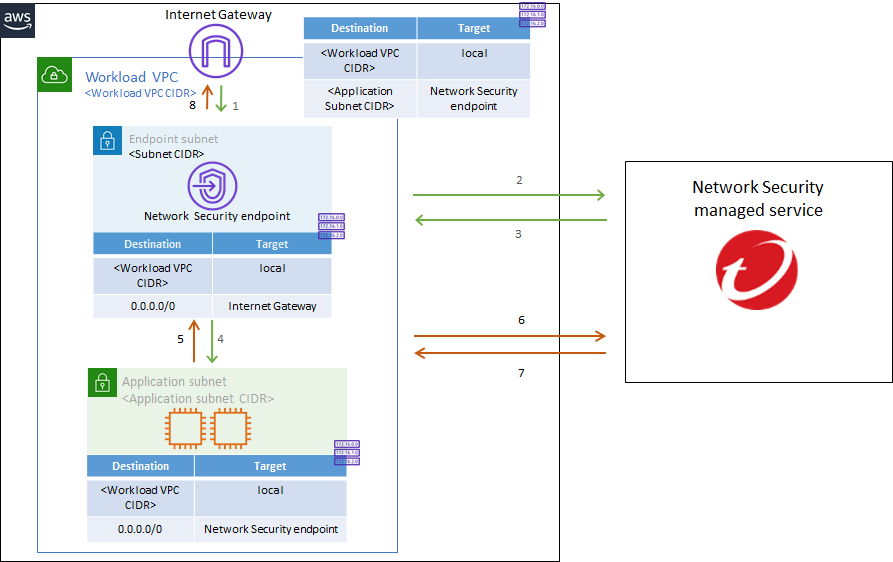
This is the deployment that we will be using in our workshop 😊
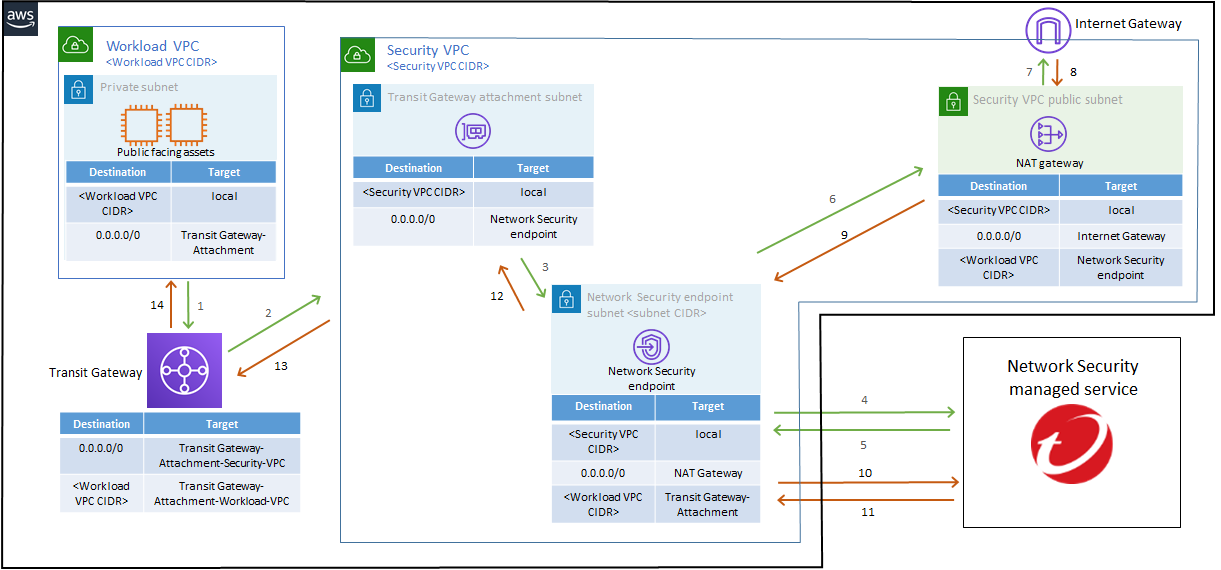
Environments that use a Transit Gateway
his configuration is best suited for cloud environments with a centralized architecture that use Transit Gateways to send traffic between different VPCs. AWS Transit Gateways are often used to support ‘hub-and-spoke’ topologies. Learn more about AWS Transit Gateways.
In this deployment type, traffic can flow from Workload VPCs, which contain public facing assets, to a centralized, shared services VPC, called the Security VPC in this example. After Network Security managed service is deployed, traffic is diverted to managed service for inspection after the traffic passes through the Security VPC.